Uniqueness and Existence for Second Order Differential Equations
Recall that for a first order linear differential equation
y' + p(t)y = g(t) y(t0) = y0
if p(t) and g(t) are continuous on [a,b], then there exists a unique solution on the interval [a,b].
We can ask the same questions of second order linear differential equations. We need to first make a few comments. The first is that for a second order differential equation, it is not enough to state the initial position. We must also have the initial velocity. One way of convincing yourself, is that since we need to reverse two derivatives, two constants of integration will be introduced, hence two pieces of information must be found to determine the constants.
A second comment is that of notation. Let
y'' + p(t)y' + q(t)y = g(t)
be a second order linear differential equation. Then we call the operator
L(y) = y'' + p(t)y' + q(t)y
the corresponding linear operator. Thus we want to find solutions to the equation
L(y) = g(t) y(t0) = y0 y'(t0) = y'0
We will state the following theorem without proof. The proof is well above the level of this course.
|
Theorem: Existence and Uniqueness Let p(t), q(t), and g(t) be continuous on [a,b], then the differential equation y'' + p(t)y' + q(t)y = g(t) y(t0) = y0 y'(t0) = y'0 has a unique solution defined for all t in [a,b]. |
Example
Find the largest interval where
(t2 - 1)y'' + 3ty' + cos t y = et y(0) = 4, y'(0) = 5
is guaranteed to have a unique solution.
Solution
We first put it into standard form
y'' + 3t/(t2 - 1)y' + (cos t)/(t2 - 1) y = et /(t2 - 1) y(0) = 4, y'(0) = 5
p, q, and g are all continuous except at t = -1 and t = 1. The theorem tells us that there is a unique solution on [-1,1].
Homogeneous Linear Second Order Differential Equations
Next we will investigate solutions to homogeneous differential equations. Consider the homogeneous linear differential equation
L(y) = 0
We have the following theorem
| Theorem
Let L(y) = 0 be a homogeneous linear second order differential equation and let y1 and y2 be two solutions. Then c1y1 + c2y2 is also a solution for any pair or constants c1 and c2. |
Using the terminology of linear algebra, we know that L is a linear transformation of the vector space of differentiable functions into itself. The theorem reminds us that the kernel of a linear transformation is a vector subspace.
Proof
L(c1y1 + c2y2) = (c1y1 + c2y2)'' + p(t)(c1y1 + c2y2)' + q(t)(c1y1 + c2y2)
= c1y1'' + c2y2'' + p(t)c1y1' + p(t)c2y2' + q(t)c1y1 + q(t)c2y2
= c1y1'' + p(t)c1y1' + q(t)c1y1 + q(t)c2y2'' + p(t)c2y2' + q(t)c2y2
= c1(y1'' + p(t)y1' + q(t)y1) + c2(y2'' + p(t)y2' + q(t)y2)
= c1L(y1) + c2L(y2) = 0 + 0 = 0.
Next, we investigate the initial conditions. If we find a general solution to the homogenous system, can we choose constants such that the solution satisfies the initial conditions? That is can we find c1 and c2 such that
c1y1(t0) + c2y2(t0) = y0
c1y1'(t0) + c2y2'(t0) = y0'
We can put this into a matrix equation
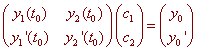
This has a unique solution if and only if the determinant of the matrix is not zero. This determinant is called the Wronskian.
This proves the following theorem
| Theorem
Let L(y) = 0 y(t0) = y0 y'(t0) = y'0 be a homogeneous linear second order differential equation and let y1 and y2 be two general solutions (No initial value. Then if the Wronskian y1y2' - y1' y2 is nonzero, there exists a solution to the initial value problem of the form y = c1y1 + c2y2 |
Example
Consider the differential equation
y'' + 2y' - 8y = 0
It is easy to check that the general solution is given by
y = c1e2t + c2e-4t
The Wronskian of
y1 = e2t y2 = e-4t
is given by
e2t(-4e-4t) - (2e2t)e-4t = -4e-2t - 2e-2t = -6e-2t
Which is never zero. We can conclude that any initial value problem will have a unique solution of the form
y = c1e2t + c2e-4t
Back to the Linear Second Order Differential Equations Home Page
Back to the Differential Equations Home Page
Back to the Math Department Home Page
e-mail Questions and Suggestions