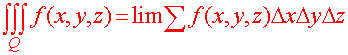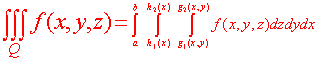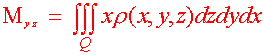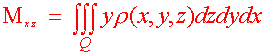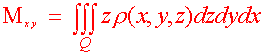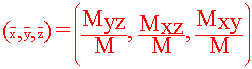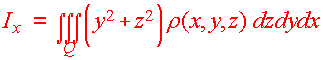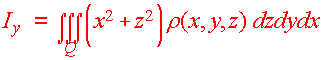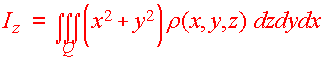Triple Integrals
Definition of the Triple Integral
We have seen that the geometry of a double integral involves cutting the two dimensional region into tiny rectangles, multiplying the areas of the rectangles by the value of the function there, adding the areas up, and taking a limit as the size of the rectangles approaches zero. We have also seen that this is equivalent to finding the double iterated iterated integral.
We will now take this idea to the next dimension. Instead of a region in the xy-plane, we will consider a solid in xyz-space. Instead of cutting up the region into rectangles, we will cut up the solid into rectangular solids. And instead of multiplying the function value by the area of the rectangle, we will multiply the function value by the volume of the rectangular solid.
We can define the triple integral as the limit of the sum of the product of the function times the volume of the rectangular solids.
Instead of the double integral being equivalent to the double iterated integral, the triple integral is equivalent to the triple iterated integral.
|
Definition of the Triple Integral Let f(x,y,z) be a continuous function of three variables defined over a solid Q. Then the triple integral over Q is defined as
where the sum is taken over the rectangular solids included in the solid Q and lim is taken to mean the limit as the side lengths of the rectangular solid. |
This definition is only practical for estimating the triple integral when a data set is given. When we have a symbolically defined function, we use an extension of the fundamental theorem of calculus which is just Fubini's theorem for triple integrals.
|
Theorem for Evaluating Triple Integrals Let f(x,y,z) be a continuous function over a solid Q defined by a < x < b h1(x) < y < h2(x) g1(x,y) < z < g2(x,y) Then the triple integral is equal to the triple iterated integral.
|
Remark: As with double integrals the order of integration can be changed with care.
Examples
Example
Evaluate
![]()
Where
f(x,y,z) = 1 - x
and Q is the solid that lies in the first octant and below the plain
3x + 2y + z = 6
Solution
The picture of the region
The challenge here is to find the limits. We work on the innermost limit first which corresponds with the variable "z". Think of standing vertically. Your feet will rest on the lower limit and your head will touch the higher limit. The lower limit is the xy-plane or
z = 0
The upper limit is the given plane. Solving for z, we get
z = 6 - 3x - 2y
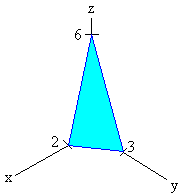
Now we work on the middle limits that correspond to the variable "y". We look at the projection of the surface in the xy-plane. It is shown below.
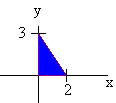
Now we find the limits just as we found the limits of double integrals. The lower limit is just
y = 0
If we set z = 0 and solve for y, we get for the upper limit
y = 3 - 3/2 x
Next we find the outer limits, corresponding to the variable "x". The lowest x gets is 0 and highest x gets is 2. Hence
0 < x < 2
The integral is thus
Example
Switch the order of integration from the previous example so that dydxdz appears.
Solution
This time we work on the "y" variable first. The lower limit for the y-variable is 0. For the upper limit, we solve for y in the plane to get
y = 3 - 3/2 x - 1/2 z
To find the "x" limits, we project onto the xz-plane as shown below
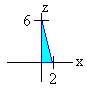
The lower limit for x is 0. To find the upper limit we set y = 0 and solve for x to get
x = 2 - 1/3 z
Finally, to get the limits for z, we see that the smallest z will get is 0 and the largest z will get is 6. We get
0 < z < 6
We can write
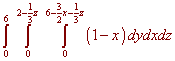
Mass, Center of Mass, and Moments of Inertia
For a three dimensional solid with constant density, the mass is the density times the volume. If the density is not constant but rather a continuous function of x, y, and x, then we can cut the solid into very small rectangular solids so that on each rectangular solid the density is approximately constant. The volume of the rectangle is
D Mass = (Density)(DVolume) = f(x,y,z) DxDyDz
Now do the usual thing. We add up all the small masses and take the limit as the rectangular solids get small. This will give us the triple integral
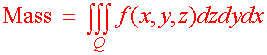
We are often interested in the center of mass of a solid. For example when the NEAR satellite orbited around the asteroid Eros, NASA scientists needed to compute the center of mass of the asteroid. Kepler told us that a stable orbit will always orbit in an elliptical orbit with the center of mass as one of the foci.
The NEAR satellite orbiting around Eros
We find the center of mass of a solid just as we found the center of mass of a lamina. Since we are in three dimensions, instead of the moments about the axes, we find the moments about the coordinate planes. We state the definitions from physics below.
|
Definition: Moments and Center of Mass Let r(x,y,z) be the density of a solid Q. Then the first moments about the coordinate planes are
and the center of mass is given by
|
Notice that letting the density function being identically equal to 1 gives the volume
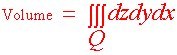
Exercise
Find the center of mass of the solid that lies below the paraboloid
z = 4 - x2 - y2
that lies above the xy-plane if the density of the region is given by
r(x,y,z) = x2 + 2y2 + z
You may use your calculator or computer to evaluate the integrals.
Just as with lamina, there are formulas for moments of inertial about the three axes. They involve multiplying the density function by the square of the distance from the axes. We have
|
Definition: Moments of Inertia Let r(x,y,z) be the density of a solid Q. Then the first moments of inertia about the coordinate axes are
|
Click here for an application to probability
Back to the Multiple Integration Home Page
Back to the Vector Calculus Home Page
Back to the Math Department Home Page
e-mail Questions and Suggestions