Descriptive Statistics and Stem and Leaf Diagrams
Stem and Leaf Diagrams
For data that we want to understand how it looks without losing the individual data points, we use a stem and leaf diagram. To construct a stem and leaf diagram, we put the first digit or more (the stem) on the left and that digit's corresponding list (leaf) on the right. We can also have the high and low of the digit. If we want to compare two data sets we can draw the digits in the middle, the first set of leaves on the right, and the second set of leaves on the left. This is useful for comparing two data sets. A comparative stem and leaf diagram is often used. The middle represents the stems, and the left and right sides are the leaves of each of the two data sets.
Example
A computer retailer collected data on the number of computers sold during 20
consecutive Saturdays during the year. The results are as follows:
12, 14, 14, 17, 21, 24, 24, 25, 25, 26,
26, 27, 29, 31, 34, 35, 36, 39, 40, 42,
42, 45, 46, 47, 49, 49, 56, 59, 62.
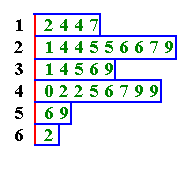
We can put this data into a stem and leaf diagram as shown below. The first digit represents the stem and the second digit represents the leaf. The stem is written on the left hand side (once per value) and the leaf is written on the right hand side next to the corresponding stem.
1|
2 4 4 7
2|
1 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 9
3|
1 4 5 6 9
4|
0 2 2 5 6 7 9 9
5|
6 9
6|
2
It is easy to see the shape of the distribution without losing any of the
individual data. To read the stem and leaf diagram, for example the first
row corresponds to all the data from 10 to 17. As shown below, the stem
and leaf is a type of histogram that retains the raw data.
Back to the Descriptive Statistics Home Page
Back to the Elementary Statistics (Math 201) Home Page