Symbols and Their Meaning
Below are the some of the symbols that represent parameters and statistics that are used in elementary statistics.
- x The
random variable that represents the quantitative outcome. For example, if
a survey is conducted asking 100 people how
much they weigh, then x is a randomly
selected respondents weight
- m The
population mean. For example, for the survey that asks
100 people's weight,
m represents the average weight of all
people in the world, not just from the survey respondents.
-
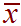 The sample mean. For example, for the survey that asks
100 people's weight,
The sample mean. For example, for the survey that asks
100 people's weight,
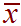 represents the average weight of the 100
respondents.
represents the average weight of the 100
respondents.
-
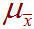 The population mean of the sampling distribution. For example,
consider every possible group of 100
people. Each one of these groups will have its own sample mean
The population mean of the sampling distribution. For example,
consider every possible group of 100
people. Each one of these groups will have its own sample mean
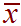 ,
the mean of all of these many many
,
the mean of all of these many many
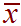 's
will be the population mean of the sampling distribution
's
will be the population mean of the sampling distribution
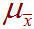 .
.
- s The
population standard deviation. For example, for the survey that asks
100 people's weight,
s represents the standard deviation of all
people in the world, not just from the survey respondents.
- s The
sample standard deviation. For example, for the survey that asks
100 people's weight,
s represents the standard
deviation of the 100 respondents.
-
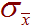 The population standard deviation of the sampling distribution. For
example, consider every possible group of 100
people. Each one of these groups will have its own sample standard
deviation
The population standard deviation of the sampling distribution. For
example, consider every possible group of 100
people. Each one of these groups will have its own sample standard
deviation
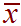 ,
the standard deviation of all of these many many
,
the standard deviation of all of these many many
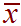 's
will be the population standard deviation of the sampling distribution
's
will be the population standard deviation of the sampling distribution
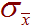 .
.
- p The population
proportion. For example, if a survey is conducted of
100 randomly selected Americans asking them
if they were born in America, then p
is the proportion of all Americans who were born in America not just the
100 Americans who were surveyed.
-
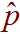 The sample proportion. For example, if a survey is conducted of
100 randomly selected Americans asking them
if they were born in America, then
The sample proportion. For example, if a survey is conducted of
100 randomly selected Americans asking them
if they were born in America, then
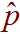 is the proportion of the 100 Americans who
were surveyed that were born in American.
is the proportion of the 100 Americans who
were surveyed that were born in American.
-
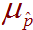 The population mean of the sampling distribution for proportions. For
example, consider every possible group of 100
people. Each one of these groups will have its own sample proportion
The population mean of the sampling distribution for proportions. For
example, consider every possible group of 100
people. Each one of these groups will have its own sample proportion
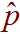 ,
the mean of all of these many many
,
the mean of all of these many many
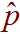 's
will be the population mean of the sampling distribution for proportions
's
will be the population mean of the sampling distribution for proportions
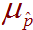 .
.
-
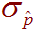 The population standard deviation of the sampling distribution for
proportions. For example, consider every possible group of
100 people. Each one of these groups
will have its own sample proportion
The population standard deviation of the sampling distribution for
proportions. For example, consider every possible group of
100 people. Each one of these groups
will have its own sample proportion
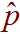 ,
the standard deviation of all of these many many
,
the standard deviation of all of these many many
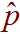 's
will be the population standard deviation of the sampling distribution for
proportions
's
will be the population standard deviation of the sampling distribution for
proportions
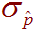 .
.