Function Algebra and Important Functions
I. Homework
II. Function notation
We write f(x) to mean the function whose input is x.
Examples:
If f(x) = 2x-3
then f(4) = 2(4) - 3 = 5
We can think of f and the function that takes the input multiplies it by 2 and subtracts 3. Sometimes it is convenient to write f(x) without the x. Thus:
f( ) = 2( ) - 3
whatever is in the parentheses, we put inside. For example:
f(x - 1) = 2(x - 1) - 3
(f(x + 4) - f(x))/4 = ([2(x + 4) - 3] - [2(x) - 3]/4 = (2x + 8 - 3 - 2x + 3)/4 = 8/4 = 2
We will try other examples.
III. Composition of functions
If f(x) and g(x) are functions then we define f o g (x) as f(g(x))
Example:
If f(x) = 4/x and g(x) = x2 - x
The f o g(x) = 4/(x2 - x)
IV. Function Arithmetic
We define the sum, difference, product and quotient of functions in the obvious way.
Example:
If f(x) = (x + 1)/(x - 1) and g(x) = x2 + 4
then
(f + g)(x) = (x + 1)/(x - 1) + (x2 + 4)
(f - g)(x) = (x + 1)/(x - 1) - (x2 + 4)
(f g)(x) = [(x + 1)/(x - 1)][(x2 + 4)]
(f /g)(x) = [(x + 1)/(x - 1) ]/ (x2 + 4)
V. Four Important Functions.
Section 11.3 discusses four important functions and their variations. A list is given below:
1) Linear Functions (lines)
You can identify a linear function as
f(x) = mx + b
their graphs can be found by plotting the y intercept and using the slope to plot the second point. A demonstration will be given in class.
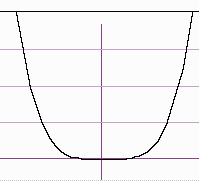
2) Quadratic functions (parabolas)
You can identify a quadratic function by the equation
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
Their pictures are parabolas. In section 9.2, we discussed how to graph a parabola in-depth.
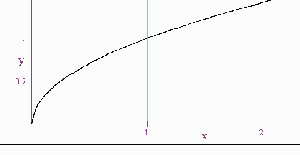
3) Square root functions:
You can identify a square root function by the equation
f(x) = sqrt(x)
They are half parabolas on their sides.
4) Absolute Value functions:
You can identify an absolute value function by the equation
y = |x|.
These look like the letter "V".
VI. Polynomials
A polynomial function is a sum of multiples of powers of x. Examples are
f(x) = 3x4 - 2x3 + x2 - 3
Their graphs are beyond the scope of this course. Other examples will be given.
VII. Graphing basic functions:
To graph a square root function we plot enough points and connect the dots making sure the shape works with the given basic shape.
Examples will be given in class.