Practice Exam 1
Please work out each of the given problems. Credit will be based on the steps that you show towards the final answer. Show your work.
Problem 1
Solve the inequality. Write the solution on a number line.
2x2 - 5x > 3
We first bring all terms to the left hand side and factor
2x2 - 5x - 3 > 0
(2x + 1)(x - 3) > 0
The key points occur when the left hand side equals 0 that is
x = -1/2 or x = 3
Cut the number line into the regions
-
to the left of -1/2
-
between -1/2 and 3
-
to the right of 3
Now set up the table
|
Test Value |
2x + 1 |
x-3 |
Total |
|
-1 |
- |
- |
+ |
|
0 |
+ |
- |
- |
|
4 |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Since the inequality is ">" we want the positive regions. We include the endpoints -1/2 and 3. Our solution is
(-![]() , -1/2]
U [3,
, -1/2]
U [3, ![]() )
)
Problem 2
Solve x1/2 + 2x1/4 - 8 = 0
Let
u = x1/4 u2 = x1/2
Substituting gives
u2 + 2u - 8 = 0
(u - 2)(u + 4) = 0
u = 2 or u = -4
Resubstituting gives
2 = x1/4 or -4 = x1/4
(2)4 = (x1/4)4 or (-4)4 = (x1/4)4
x = 16 or x = 256
Now we verify that 16 is a solution, however plugging 256 back in doe not yield 0. Hence the only solution is x = 16.
Problem 3
Solve
![]()
First isolate the square root sign
![]()
Now square both sides
x - 3 = (3 - x)2 = x2 - 6x + 9
x2 - 7x + 12 = 0 bringing to the right and combining like terms
(x - 3)(x - 4) = 0 factoring
x = 3 or x = 4
Notice that plugging in 3 works while plugging in 4 does not work. The solution is x = 3.
Problem 4 The graph of y = x2 + 2 is shown below. Find the equation of the other parabola.

Solution
The other graph is the same as the original graph but shifted to the right by 3 units. Hence the equation is
y = (x - 3)2 + 2
Problem 5
Find the domain and range of
y = x2 + 5
Solution
This is a concave up parabola with
vertex at (0,5). Since any number is a valid
input of this function, the domain is (-![]() ,
,![]() ).
The range begins at 5 and then continues
indefinitely, that is, the range is [5,
).
The range begins at 5 and then continues
indefinitely, that is, the range is [5,![]() ).
).
Problem 6
Find the domain of
x2 - 5x - 1
x3 - 3x2
+ 2x
The domain of a rational function is the set of all x such that the denominator is nonzero.
x3 - 3x2
+ 2x
x(x2 - 3x + 2) = 0
x(x - 2)(x - 1) = 0
x = 0, x = 2, or x = 1
so the domain is
{x| x ![]() 0,
x
0,
x ![]() 2, x
2, x
![]() 1}
1}
Problem 7
Answer the following True or False. If True, explain your reasoning, if False, explain your reasoning or show a counter-example.
A. (7 Points) All parabolas y = ax2 + bx + c are graphs of functions.
True, since these parabolas pass the vertical line test.
B. (7 Points) If the vertex of the parabola y = ax2 + bx + c has positive y-coordinate and the parabola is concave up, then the parabola has two x-intercepts.
False, it will have no x-intercepts. For example, y = x2 + 1 has no x-intercepts.
C. (7 Points) If a graph has two y-intercepts then the graph is not the graph of a function.
True, is it has two y-intercepts then there are two y values that come from the same x value.
Problem 8
If
f(x) = x2 - x and g(x) = 2x + 1
find
A. gog -1(x)
Solution
This is always x, since the function of its inverse is always x.
B. f.g(2)
We have
f(2) = 22 - 2 = 2
and
g(2) = 2(2) + 1 = 5
so that
f.g(2) = (2)(5) = 10
B. gof(3)
We have
f(3) = 32 - 3 = 6
and
gof(3) = g(6) = 2(6) + 1 = 13
C. fof(x)
fof(x) = f(x2 - x) = (x2 - x)2 - (x2 - x)
= x4 - 2x3 + x2 - x2 + x
= x4 - 2x3 + x
Problem 9
Use the graphs to find gof(1)

Solution
The graph shows us that
f(1) = 3
so that
gof(1) = g(3)
The graph of g goes through the x-axis at this point hence
g(3) = 0
Problem 10
The graph of f(x) is shown below. Sketch the graph of f -1(x).

Solution
The inverse graph is just the original graph reflected about the line y = x.

Problem 11
If the graph of f(x) = bx passes through (2,16), find f(3).
Solution
We have
16 = b2
so that
b = 4
Hence
f(3) = 43 = 64
Problem 12
Graph the quadratic function. Label any intercepts, the vertex, and the axis of symmetry.
y = -2x2 + 4x + 6
The x-coordinate of the vertex is
x = -b/2a = -4/-4 = 1
Now plug 1 into the equation to get
y = -2(1)2 + 4(1) + 6 = 8
Hence the vertex is at (1,8).
To find the y-intercept plug in 0 for x to get
(0,6)
To find the x-intercept, plug in 0 for y to get
0 = -2x2 + 4x + 6
0 = x2 - 2x - 3 Dividing by -2
0 = (x - 3)(x + 1) Factoring
x = 3 or x = -1 The zero product rule
The x-intercepts are
(3,0) and (-1,0)
Notice that the coefficient of x2 is negative, so the graph is concave down. Now plot the points and sketch the graph.

Problem 13
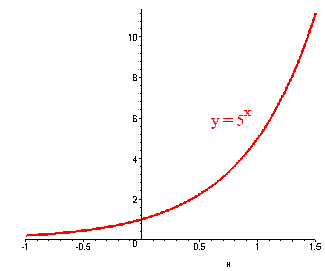
Sketch the graph of y = 5x.
Solution
This is an exponential function. We first find a few points.
| x | 0 | 1 | -1 |
| y | 1 | 5 | 1/5 |
The graph is shown below
Problem 14
Solve for w in
22w = 1/256
Solution
We turn this into a log equation to get
2w = log2(1/256) = -log 256
This log is 8 (powers of 2 are 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256) hence
2w = -8
or
w = -4
Problem 15
When a certain radioactive element decays, the amount to the element A at any time t is given by
A = 25 (2t/1500)
How much of the element will be left after 3000 years?
Solution
We plug 3000 into this equation for t to get
A = 25 (23000/1500) = (25)22 = 100
Problem 16
One muffin, two pies, and three cakes cost $23. One Muffin, three pies , and two cakes cost $21. One muffin, four pies, and five cakes cost $39. Find the cost of each.
SolutionLet
x = the cost per muffin
y = the cost per pie
z = the cost per cake
We get three equations:
x + 2y + 3z = 23
x + 3y + 2z = 21
x + 4y + 5z = 39
Subtracting the second equation from the first gives
-y + z = 2
Subtracting the second equation from the third gives
y + 3z = 18
Now add the two equations above to get
4z = 20
z = 5 dividing by 4
Plugging z = 5 back into the equation above to get
y + 3(5) = 18
y = 3 subtracting by 15
Now plug in y = 3 and z = 5 into the first original equation to get
x + 2(3) + 3(5) = 23
x + 21 = 23 6 + 15 = 23
x = 2 Subtracting 2 from both sides
Now plug in (2,3,5) into the second and third equations to check.
2 + 3(3) + 2(5) = 21
2 + 4(3) + 5(5) = 39
We can conclude that the muffins cost $2, the pies cost $3, and the cake costs $5.