Name
.
Math 152B
Practice Exam 3
Please do all
of the following problems. All work
and all answers must be done on your own paper.
Credit earned will be based on the steps that you show that lead to the
final solution. Good Luck!
Problem
1:
Write
down the quadratic formula
If
ax2 + bx + c = 0
then
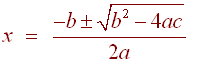
Problem
2:
Find
the root:
![]()
-2, since (-2)3 = -8
Problem
3: Simplify the expression. Leave
your answer in exponential form with only positive exponents.
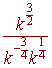
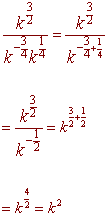
Problem
4:
Use
the discriminant to determine the nature of the roots of the following
quadratics.
A.
2x2
+ 3x + 4 = 0
The discriminant is
32 - 4(2)(4) = 9 - 32 < 0
Since
the discriminant is negative, we can conclude that there are no real roots, only
two complex conjugate roots.
B.
3x2
+ x - 4 = 0
The discriminant is
12 - 4(3)(-4) = 1 + 48 > 0
Since the discriminant is positive, we can conclude that there are two distinct real roots.
C.
4354324532453x2 + 2x + 6798797698766 = 0
The discriminant is two difficult to compute by hand, however we see that the second coefficient is small in comparison to the other two coefficients, that is
22 - 4(big)(big) = 4 - very big < 0
Since
the discriminant is negative, we can conclude that there are no real roots, only
two complex conjugate roots.
Problem
5:
Multiply and Simplify
![]()

Problem
6:
Solve
the equation by using the factoring or root method.
A)
10x2
= 13x + 3
First bring all terms to the left hand side
10x2 - 13x - 3 = 0
There are two ways of completing this problem. The first is to use the quadratic formula
a = 10 b = -13 c = -3

Hence
13 + 17
x =
20
or
13 - 17
x =
20
We get x = 3/2 or x = -1/5
Alternatively, we can factor using the AC method:
AC = -30
The two numbers that multiply to -30 and add to -13 are
(-15,2)
We now rewrite
= 5x(2x - 3) + 1(2x - 3) Factoring by grouping
= (5x + 1)(2x - 3) = 0
Hence
5x + 1 = 0 or 2x - 3 = 0
x = -1/5 or x = 3/2
B) 2x2 + 15 = 11
To solve this, there is no "x" term, so we can use the square root property:
2x2 = -4 Subtracting 15 from both sides
x2 = -2 Dividing both sides by two
x =
![]()
![]() i
Taking the square root of both sides and pulling
out an i
i
Taking the square root of both sides and pulling
out an i
Problem
7:
Solve the following by completing the square
5x2 - 20x + 21 = 0
5(x2 - 4x) + 21 = 0 Pulling out the 5 from the first two terms
Now calculate the magic number (b/2)2
(-4/2)2 = (-2)2 = 4
5(x2 - 4x + 4 - 4) + 21 = 0 Adding and subtracting the magic number 4
5[(x - 2)2 - 4] + 21 = 0 Factoring the first three terms
5(x - 2)2 - 20 + 21 = 0 Distributing the 5 through
5(x - 2)2 + 1 = 0 Adding the numbers
5(x - 2)2 = -1 Adding the numbers
(x - 2)2 = -1/5 Dividing both sides by 5
x - 2 =
![]() i
/
i
/![]() Taking
the square root of both sides and pulling out an i
Taking
the square root of both sides and pulling out an i
x = 2
![]() i
/
i
/![]() Adding
2 to both sides
Adding
2 to both sides
x = 2
![]() i
i![]() /5
Rationalizing
the denominator
/5
Rationalizing
the denominator
Problem
8:
Solve the following using the quadratic formula
6x2 + 5x - 4 = 0
We use the quadratic formula with
a = 6, b = 5, c = -4

So that
x = 1/2 + 11/12 or x = 1/2 - 11/12
Notice that we could have instead used the AC method to factor.
Problem
9 Simplify the expression. Assume
all variables represent positive real number.
![]()
Solution
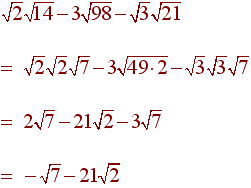
Problem 10 Multiply and Simplify
![]()

5
4 -
![]()
5 (4 +
![]() )
)
( 4 - ![]() )(4 +
)(4 +
![]() )
)
20 + 5![]()
=
16 - 6
20 + 5![]()
=
10
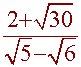

![]()
Solution
First isolate the first root by adding the square root of x to both sides.
![]()
Next square both sides. Do not forget to FOIL out the right hand side.

Now isolate the square root of x. Subtract x + 9 from both sides to get
![]()
Divide by -6:
![]()
Finally square both sides to get
x = 1
Put x = 1 back into the original equation to see if it works:
![]()
So x = 1 is the solution.
Problem 14 Solve the compound inequality
2x - y > 4
2x + 3y < 6
Solution
Graph the two lines first. Notice that the first should be graphed as a dashed line, since the sign is a ">" so equality makes it false. The second will be a solid line, since equality makes is true. We construct two T-tables
|
|
Now graph the two lines:
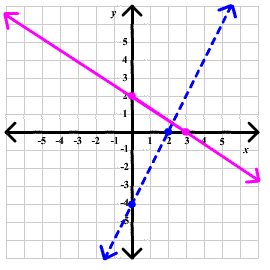
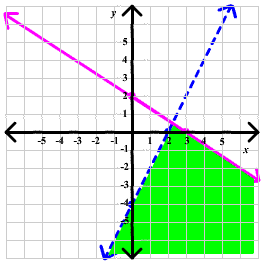
Now we use the origin as a test point for both lines. For the blue line, we have
2(0) - 0 > 4
is false so we include points below the blue line
For the pink line, we have
2(0) + 3(0) < 6
is true, so we include points below the pink line. Below is the graph of the solution.
Back to the Factoring and Rational Expressions Page
Back to the Basic Algebra Part II Page
Back to the Math Department Home Page
Questions, Comments and Suggestions Email: greenl@ltcc.edu