Powers of Trig Functions
-
Powers of Sin and Cos
Example:
Evaluate int sin5x dx we write
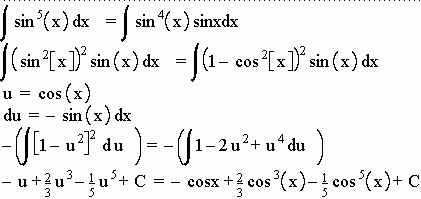
Exercise: int cos7x dx
Example: Evaluate int sin4x dx
Solution: We write int sin4x dx = int (sin2x)2 dx
= int (1/2 - 1/2 cos(2x))2 dx
= int 1/4 - 1/2 cos(2x) + 1/4 cos2(2x) dx For the second integral let u = 2x dx = 1/2du
= 1/4 x - 1/4 sin(2x) + 1/4 int 1/2 + 1/2 cos(4x) Let u = 4x dx = 1/4du
= 1/4 x - 1/4 sin(2x) + 1/8 x + 1/32 sin(4x) + C
We see that if the power is odd we can pull out one of the sin functions and convert the other to an expression involving the cos function only. Then use u = cos x.
If the power is even, we must use the trig identities
sin2x = 1/2 - 1/2 cos(2x)
and
cos2x = 1/2 + 1/2 cos(2x)This method will always work and is always long and tedious.
-
Mixed powers of Sin and Cos
Example: Evaluate
int sin2x cos3x dx. We pull out a cos x and convert the cos2 x to 1 - sin2 x:
int sin2x (1 - sin2 x) cosx dx Let u = cosx, du = -sinx dx
We have
int u2(1 - u2)du = int u2 - u4 du = 1/3 u3 - 1/5 u5 + C
= 1/3 cos3x - 1/5 cos5x + C
Exercise: int sin5x cos2x dx
-
Powers of Tangents and Secants
To integrate powers of tangents and secants we use the formula
tan2 x = sec2 x - 1
Example: Evaluate int tan4 x dx
Solution: We write int tan2 x tan2 x dx = int tan2 x (sec2 x - 1)
= int tan2 x sec2 x dx - int tan2 x dx = int tan2 x sec2 x dx - int (sec2 x - 1) dx
For the first integral let u = tan x du = sec2 x dx.
We have int u2 du - tanx - x
= 1/3 u3 - tanx - x + C
= 1/3 tan3 x - tan x - x + C
Exercise: int sec5 x tan3 x dx.
-
Mixed Angles
We have the following formulas:
sin(mx) sin(nx) = 1/2[cos[(m - n)x] - cos[(m + n)x]]
sin(mx) cos(nx) = 1/2[sin[(m - n)x] + sin[(m + n)x]]
cos(mx) cos(nx) = 1/2[cos[(m - n)x] + cos[(m + n)x]]
Example:
int sin(3x)sin(4x)dx = 1/2 int cos(-x) - cos(7x) dx
We integrate the first by letting u = -x and the second by letting u = 7x.