The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
I. Quiz
II. Homework
III. The Mean Value Theorem For Integrals
Let f be continuous on [a,b] then there is a c in [a,b] such that
int from a to b of f(x) dx = f(c)(b - a)
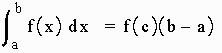
We define the average value of f(x) between a and b as
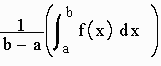
Example: The average value of sin x between 0 and pi is
1/(pi - 0)int from 0 to pi of sinx dx = 1/(pi - 0)[-cosx]from 0 to pi
= (1/pi)(1 + 2) = 2/pi
V. The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Let f be continuous on [a,b] then
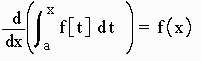
A Proof will be given in class.
Exercise:
d/dx int from 3 to x of tt = xx
Exercise:
d/dx int from 5 to x2 of sqrt(1 + t2 )dt let y = int from 5 to u of sqrt(1 + t2 )dt and u = x2
then dy/dx = dy/du du/dx = sqrt(1 + u2)(2x) = sqrt(1 + x4 )2x.
Example: Let

If g(x) is the inverse of f(x), find g'(0)
Solution: We can use the formula
g'(0) = 1/f'(g(0)
By the second fundamental theorem of calculus, f'(x) = sin2(x). To find g(0) we note that an integral is 0 when a = b. Hence g(0) = 3. Finally
g'(0) = 1/f'(3) = 1/sin2(3) approx 50.