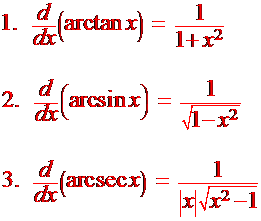Inverse Trigonometric Derivatives
Definition of the Inverse Trig Functions
Recall that we write
arcsin
x
to mean the inverse sin of x restricted to have
values between -p/2 and
p/2 (Note that
sin x does not pass the horizontal
line test, hence we need to restrict the domain.) We define the other
five inverse trigonometric functions similarly.
Trig of Arctrig Functions
Example:
Find tan(acrsin(x))
![]()
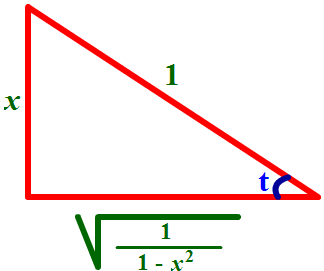
The triangle above demonstrates that
sin(t) = x/1 = opp/hyp.
Hence
![]()
Since the tangent is
opp/adj
We have
|
|
Exercise
Simplify
cos(arctan(2x))
![]()
Derivatives of the Arctrigonometric Functions
Recall that if f and g are inverses, then
![]()
What is
d
arctan(x)
dx
We use the formula:
![]()
Since
opp
x
tan(q) =
=
adj 1
we
have
![]()
so that
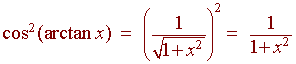
|
Theorem
|
Recall that
cos x
= sin(p/2 - x)
hence
arccos
x = p/2 - arcsin x
so
d/dx(arccos
x) = d/dx[p/2 - arcsin x]
= -d/dx[arcsinx] =
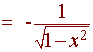
Similarly:
d/dx(arccot(x)) = -1/(1 + x2)
d/dx(arccscx)
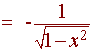
Example
Find the derivative of
cos(arcsinx)
Solution:
let
y = cosu,
u = arcsinx
y' = -sin
u
= -sin(arcsin
x) = x
![]()
We arrive at
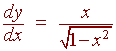
Back to the Math Department Home
e-mail Questions and Suggestions