Optimization
I. Quiz
II. Homework
III. Optimization
Steps for solving:
1) Draw the picture and label variables
2) Determine a constraint equation (if necessary) and a maximizing (minimizing) equation.
3) Use the constraint equation to solve for one of the variables and substitute it into the maximizing (minimizing) equation.
4) Take a derivative and set it equal to zero. Solve
5) Answer the question
Example: You want to construct a can that holds 150 cubic inches of juice as cheaply as possible. The top and bottom costs .1 cents per square inch and the side costs .09 cents per square inch. What should the dimensions of the can be?
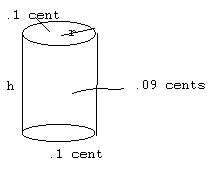
Solution: 150 = pi r2h and Cost = 2pi r2(.1) + 2pi rh(.09)
The volume equation gives us:
h = 150/pi r2 so that
C = .2pi r2 + .18pi r(150/pi r2)
= .2pi r2 + 27/r
To find the minimum cost we take the derivative and set it equal to 0:
C' = 4pi r - 27/r2 = 0
So that
4pi r3 = 27
or
r3 = 27/4pi
r = 2.14in
so that h = 150/pi(2.142) =10.4 in
Another example:
A lifeguard swims at a rate of 5 feet per second and can run at a rate of 15 feet per second. Suppose that the lifeguard spots a drowning child in the ocean 200 feet down the shore and 50 feet out at sea. How far should the lifeguard run until (s)he begins swimming?
Exercises:
A) A poster is to have an area of 120 square inches with one inch margins at the bottom and sides and a 2 inch margin at the top. What dimensions will give the largest printed area?
B) A quarter mile race track is to be designed by having a rectangle with semicircles on each end. Find the dimensions that will make the area of the rectangle as large as possible.