ANTIDERIVATIVES
Definition
Suppose that F'(x) =
f(x). Then F(x)
is called an antiderivative
of f(x).
Examples
-
An antidervative of sin(x) is -cos(x).
-
An antiderivative of x2 is 1/3 x3
Suppose we want to find the solution to
dy/dx = f(x)
This is another way of asking for an antiderivative of f.
Example
Find the solution to the differential equation
dy/dx = 3x2
- 4x + 2
Solution
We find the antiderivative of
3x2
- 4x + 2
We can find this antiderivative by finding the antiderivative of x2,
x, and 2 individually
and then subtracting and adding. We have
| Function | x2 | x | 2 |
| Antiderivative | 1 3 |
1 2 |
2x |
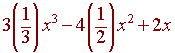
= x3
- 2x2 + 2x
Notice that since the derivative of a constant is zero, adding a constant of
an antiderivative results in another antiderivative for the same
function. We can write the final answer as
x3
- 2x2 + 2x + C
where C represents any constant.
Notation
The antiderivative of f(x) will be denoted by
![]()