Name
MATH 105 FINAL
Please work out each of the given
problems. Credit will be based on
the steps that you show towards the final answer.
Show your work.
PROBLEM 1 Please answer the following true or false. If false, explain why or provide a counter example. If true, explain why.
A) If
f(x) is a differentiable function that passes through the origin
such that f '(x) > 2
for all x,
then
f(5) cannot equal 10.
Solution
True, by the Mean Value Theorem, if f(5) = 10 then there is a c between 0 and 5 with
f(5) - f(0) 10
- 0
f '(c)
=
=
= 2
5 -
0
5
B) If
f(x) is a continuous function such that f
'(0) = 2, f '(1) = 0, and
f '(2) = -3 then f(x)
has a relative maximum at x
= 1.
False,
The first derivative test needs that within a neighborhood of x
= 1 all
values to the left have positive derivative and all
values to the right have negative derivative.
C) Suppose that h(x) = g '(x) and that f(x) and h(x) are continuous. Then if g(a) = g(b),
![]()
True, use u-substitution with u = g(x), du = g '(x), then when x = a, u = g(a) and when x = b, u = g(a) also. Since the bottom and top limit are the same, the integral is zero.
PROBLEM 2 Find the derivative of
A.
f(x) = x cos(x2)
Solution
We use the product and chain rule. Since the derivative of
cos(x2)
is
(2x)(-sin(x2)) = -2x sin(x2)
The product rule gives
f '(x) = (x)(-2x sin(x2)) + (1)(cos(x2)) = -2x2 sin(x2) + cos(x2)
B.
x2 - 1
f(x)
=
x2 + 1
Use the quotient rule
(x2 + 1)(2x) - (x2 - 1)(2x)
f '(x)
=
(x2 + 1)2
2x3 + 2x - 2x3 + 2x
=
(x2 + 1)2
4x
=
(x2 + 1)2
PROBLEM 3 Find the limit if it exist
![]()
Multiply numerator and denominator by the conjugate

PROBLEM 4 Evaluate the following integrals.
A)
![]()
Solution
Let u = x2 - 2x + 6, du = (2x - 2)dx, (x - 1)dx = du/2
When x = 1, u = 5 and when x = 3, u = 9.
We get

B)
![]()
First FOIL out and then integrate:
![]()
PROBLEM 5 (35 Points) You have a camera that rotates automatically positioned 400m from the space shuttle launch pad. When the space shuttle is 300m from the ground the shuttle is moving at 20 meters per second. How fast should your camera rotate at that instant?
First we sketch the picture and label variables

Now use the trigonometry formula:
tan q = y/400
Now take the derivative of both sides with respect to t:
sec2q dq/dt = 1/400 dy/dt
Next plug in y = 300 and use the triangle to find sec2q. Note that this is a 300-400-500 triangle, so that
sec2q = (5/4)2
We have
(25/16)dq/dt = (1/400) 20 = 1/20
Hence
dq/dt =(1/20)(16/25) = 4/125 radians per second
PROBLEM 6 (35 Points) Use right sums with n = 200 to approximate the area under the curve y = 2x + 1, above the x-axis between x = 4 and x = 10.
We have

PROBLEM 7 (35 Points) Let
![]() Find F '(x).
Find F '(x).
We use the chain rule, a property of integrals and the second fundamental theorem of calculus:
u = 1 - x2 u' = -2x

Putting this all together gives
F '(x) = (-2x)(-ln(u2 + 1)) = 2x ln[(1 - x2)2 + 1]
PROBLEM 8 (35 Points) Use the limit definition of the derivative to find the derivative of
f(x) = x2 - 2x

PROBLEM 9 Let
1
f(x) =
1 - x2
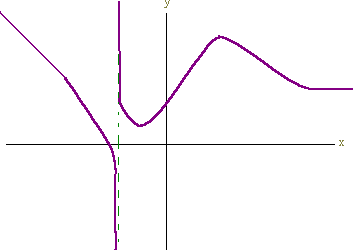
Determine any relative extrema, inflection points, intervals where y = f(x) is increasing, intervals where y = f(x) is concave up, and any asymptotes. Then use this information (not you calculator!) to graph the function.
We have
f '(x) = 2x(1 - x2) -2
Hence there is a critical point at (0,1). There are also vertical asymptotes at
x = 1 and x = -1
For x < -1, f '(x) < 0
For -1 < x < 0, f '(x) < 0
For 0 < x < 1, f '(x) > 0
For 1 < x, f '(x) > 0
Hence
the graph is decreasing on (-![]() ,
-1) U (-1, 0)
,
-1) U (-1, 0)
and
increasing on (0, 1) U (1, ![]() )
)
By the first derivative test, there is a minimum at (0,1).
We have
f ''(x) = 2(1 - x2) -2 + (2x)(-2x)(-2)(1 - x2) -3
2(1 - x2) -2 + (8x2)(1 - x2) -3
= (1 - x2) -3 [2 - 2x2 + 8x2]
= (1 - x2) -3 [2 + 6x2]
Since f ''(x) is never zero there are no inflection points. We can check for concavity:
When x < -1, f ''(x) < 0
When -1 < x < 1, f ''(x) > 0
When 1 < x, f ''(x) < 0
So the
graph is concave down on (-![]() ,
-1) U (-1,
,
-1) U (-1, ![]() )
and concave up on (-1, 1).
The graph is shown below:
)
and concave up on (-1, 1).
The graph is shown below:

PROBLEM 10
Below is the graph of y = f(x) . Sketch the graph of y = f '(x).