The Product and Quotient Rules
The Product Rule
|
Theorem (The Product Rule) Let f and g be differentiable functions. Then [f(x) g(x)] ' = f(x) g '(x) + f '(x) g(x)
|
Proof:
We have
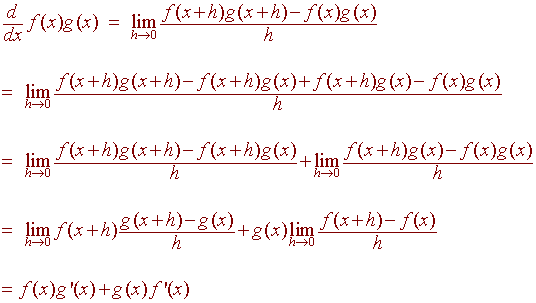
Example
Find
d
(2 - x2)(x4 - 5)
dx
Solution:
Here
f(x) =
2 - x2
and
g(x) =
x4 - 5
The product rule gives
d
(2 - x2)(x4 - 5)
= (2 - x2)(4x3) +
(-2x)(x4 - 5)
dx
The Quotient Rule
Remember the poem
"lo d hi minus hi d lo square the bottom and away you go"
This poem is the mnemonic for the taking the derivative of a quotient.
|
d
f g f
' - f g ' |
Example:
Find y' if
2x - 1
y' =
x + 1
Solution:
Here
f(x) = 2x - 1
and
g(x) = x + 1
The quotient rule gives
(x + 1)(2) - (2x - 1)(1)
(x + 1)2
2x + 2 - 2x + 1
=
(x + 1)2
3
=
(x + 1)2
Other Derivative Sites
Product Rule Problems and Solutions
Quotient Rule Problems and Solutions